
Java Architecture
Java Architecture explains how a Java program is created, compiled, and executed on different systems. It describes the internal structure of Java and the role of components like JDK, JRE, JVM, Class Loader, Memory Areas, and Execution Engine.
Understanding Java Architecture helps beginners clearly see why Java is platform independent and how Java programs run internally.
What Is Java Architecture?
Java Architecture is a layered structure that shows how Java source code is converted into machine-specific instructions and executed safely and efficiently on any operating system.
Java follows the principle:
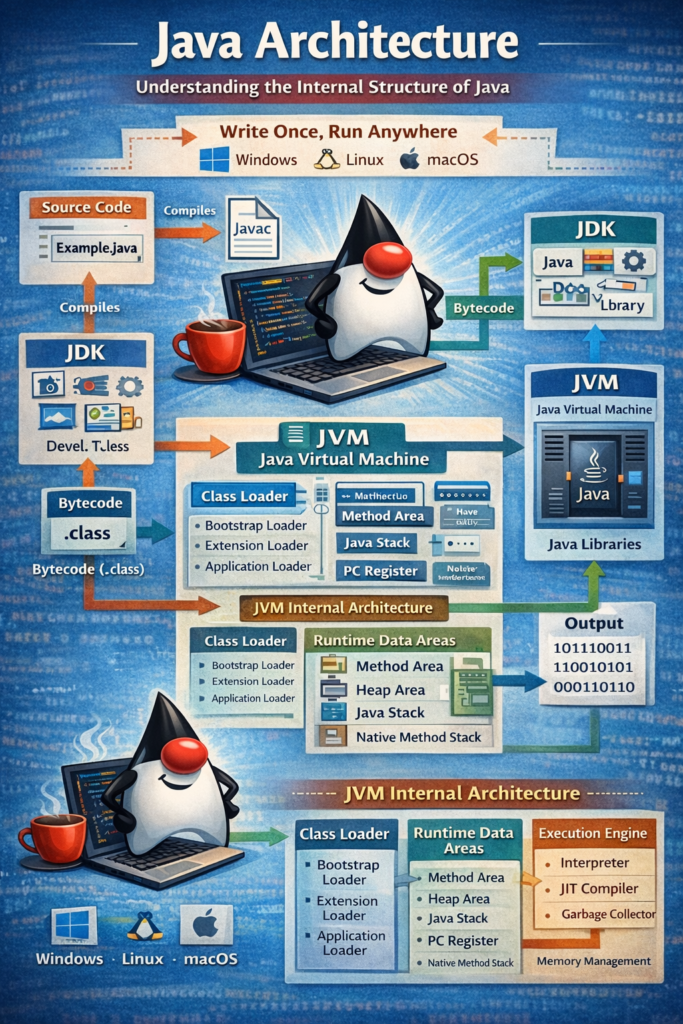
Write Once, Run Anywhere
This is possible because Java programs run on the Java Virtual Machine (JVM) instead of directly running on the operating system.
High-Level Java Architecture Flow
The execution of a Java program follows these steps:
Write Java source code (
.java)Compile using JDK compiler (javac) → generates bytecode (
.class)Bytecode is loaded into JVM
JVM converts bytecode into machine code
Program output is displayed
Main Components of Java Architecture
Java Architecture mainly consists of:
JDK (Java Development Kit)
JRE (Java Runtime Environment)
JVM (Java Virtual Machine)
Let’s understand each component in detail.
1. Java Development Kit (JDK)
JDK is used by developers to create Java applications.
JDK includes:
JRE
Java compiler (
javac)Debugger
Development tools
Purpose of JDK:
Write Java programs
Compile source code
Run Java applications
👉 Without JDK, Java development is not possible.
2. Java Runtime Environment (JRE)
JRE provides the environment required to run Java applications.
JRE includes:
JVM
Core Java libraries
Supporting runtime files
Purpose of JRE:
Execute Java programs
Provide necessary class libraries
📌 JRE cannot compile code, it can only run Java applications.
3. Java Virtual Machine (JVM)
JVM is the heart of Java Architecture. It executes Java bytecode and makes Java platform independent.
Key responsibilities of JVM:
Loads bytecode
Verifies code for security
Executes instructions
Manages memory
Handles garbage collection
📌 JVM is platform dependent, but Java bytecode is platform independent.
Internal Architecture of JVM
JVM consists of three main parts:
Class Loader Subsystem
Runtime Data Areas (Memory)
Execution Engine
1. Class Loader Subsystem
The Class Loader loads .class files into JVM memory.
Types of Class Loaders:
Bootstrap Class Loader – loads core Java classes
Extension Class Loader – loads extension classes
Application Class Loader – loads application classes
Before execution, JVM verifies bytecode to ensure security.
2. Runtime Data Areas (JVM Memory)
These are memory areas used during program execution.
Main memory areas:
Method Area – stores class-level data
Heap Area – stores objects and instance variables
Stack Area – stores method calls and local variables
PC Register – stores current instruction
Native Method Stack – supports native methods
3. Execution Engine
Execution Engine executes the bytecode.
Components:
Interpreter – executes bytecode line by line
JIT Compiler – converts bytecode into machine code
Garbage Collector – removes unused objects
Why Java Architecture Is Platform Independent
Java Architecture uses JVM as an abstraction layer between Java programs and the operating system.
Same bytecode runs on different OS
JVM converts bytecode into OS-specific machine code
No need to rewrite Java programs
This makes Java portable and flexible.
Advantages of Java Architecture
Platform independent
Secure execution environment
Efficient memory management
High performance with JIT
Robust and reliable execution
Where Java Architecture Is Used
Java Architecture is used in:
Web applications
Android development
Enterprise systems
Cloud applications
Big data platforms
Conclusion :
Java Architecture plays a crucial role in making Java one of the most reliable and widely used programming languages. By using components like JDK, JRE, and JVM, Java ensures platform independence, security, and high performance.
Understanding Java Architecture gives learners a strong foundation and helps them write efficient and optimized Java programs.
At Easy Hai Code, we explain complex Java concepts in a simple and practical way so that learning Java becomes easy and enjoyable.