JDK vs JRE vs JVM
When you start learning Java, you will often hear three terms: JDK, JRE, and JVM. They work together to help Java programs run smoothly, but each one has a different role. Let’s understand them one by one
What is JVM (Java Virtual Machine)?
JVM is the heart of Java. It is responsible for running Java programs.
JVM executes bytecode, not Java source code directly
It makes Java platform independent
Same Java program can run on Windows, Linux, or Mac
Main Responsibilities of JVM:
Loads bytecode (
.classfile)Verifies code for security
Converts bytecode into machine code
Manages memory (Heap & Stack)
Handles Garbage Collection
Important:
JVM is platform dependent (each OS has its own JVM).
What is JRE (Java Runtime Environment)?
JRE provides the environment needed to run Java applications.
It includes:
JVM
Core Java libraries
Supporting files required at runtime
When do you need JRE?
If you want to run Java programs
If you are not writing or compiling code
📌 Note:
JRE cannot compile Java programs.
What is JDK (Java Development Kit)?
JDK is a complete package used by Java developers.
It includes:
JRE
Compiler (
javac)Debugger
Development tools
When do you need JDK?
If you want to write, compile, and run Java programs
Required for Java development
📌 Note:
JDK is mainly for developers, while JRE is for users.
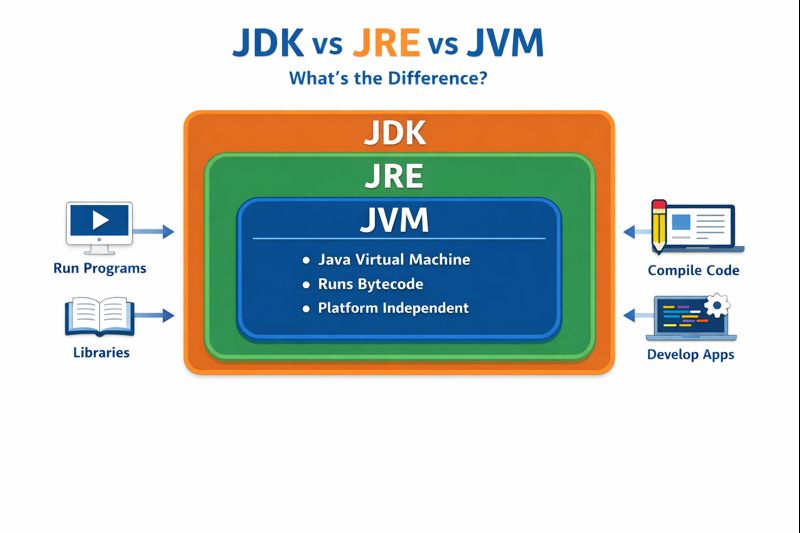
Relationship Between JDK, JRE & JVM
JDK contains JRE
JRE contains JVM
JVM runs the program
Conclusion :
In summary, JDK, JRE, and JVM work together to make Java programs possible. The JDK is used by developers to write and compile Java code, the JRE provides the required environment to run Java applications, and the JVM acts as the engine that executes Java bytecode on any platform. This layered structure is what makes Java powerful, secure, and platform independent. Understanding the difference between these three components is essential for every Java learner, as it builds a strong foundation for further Java development.